Simple and effective.
Heart screenings can detect heart issues in young student athletes before it’s too late.
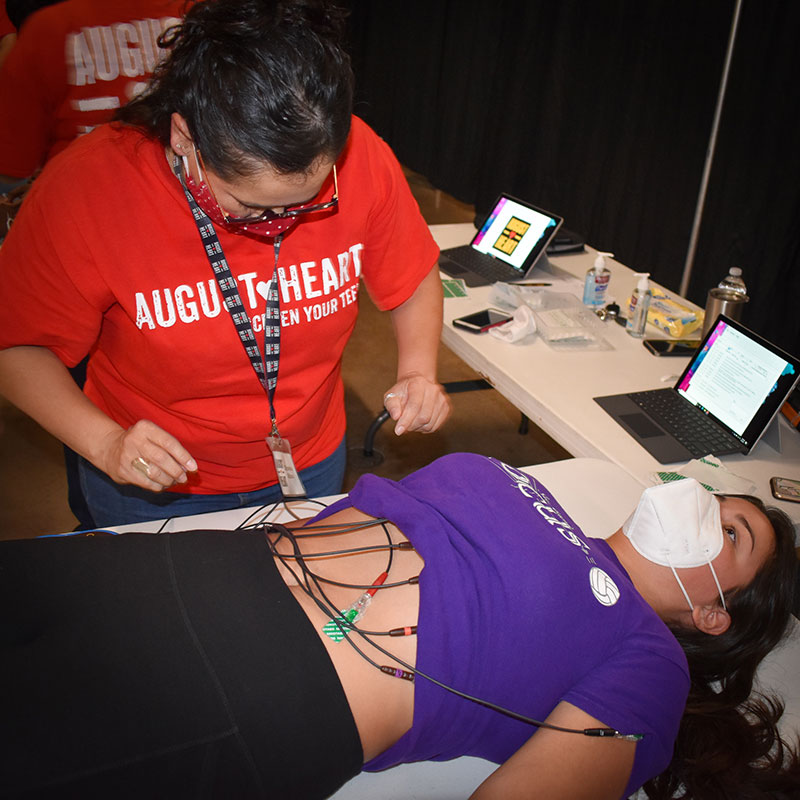
During each screening, we perform an electrocardiogram (ECG) on every student and, if necessary, an echocardiogram (ECHO).
Screenings are administered by certified ECHO sonographers and ECG technicians. These simple, non-invasive tests allow skilled cardiologists to evaluate the structure and electrical activity of the heart to identify students who might be at risk of a cardiac event. Upon review, any teenager having an abnormal screen may be offered the opportunity to undergo a more thorough evaluation so that a plan for care can be established. We assure each teenager’s confidentiality, privacy and individual modesty is respected throughout all aspects of the screening.
What we screen for
These conditions represent some of the more common causes of why children and young adults might die suddenly.
This is a problem of the heart muscle where the bottom chambers (or ventricles) are too thick. The risk of this condition has been reported to be as frequent as 1 in 500 individuals. While most of these cases are caused by high blood pressure, a genetic problem of the heart can also cause this and can lead to serious arrhythmias and/or heart failure.
This is a problem where the heart muscle is too large and does not squeeze like it is supposed to. There are many causes of this problem, including viral infections, toxic exposures, and genetic problems. The risk of this condition is estimated to be 1 in 2,000 individuals.
This is a problem of the electricity of the heart that is caused by an abnormal connection between the top and bottom pumping chambers. This condition can cause very fast heartbeats and rarely an unstable heart rhythm. The risk of this condition has been reported to be as frequent as 1 in 1,500 individuals. WPW is a congenital disorder of the heart.
This is a problem of the electricity of the heart that is caused by an issue with how the heart muscle handles essential elements like sodium and potassium. Children with this condition can suddenly develop unstable heart rhythms. Most cases are caused by a genetic problem, though some are caused by certain medications. The risk is as high as 1 in 5,000 individuals.
In 2017, experts in the areas of cardiology and sports medicine from around the world identified features on a screening electrocardiogram that they felt potentially increased the risk of a sudden cardiac event in athletes. Some of those features are found in the conditions noted above and are well established as significant issues. Others, such as arrhythmias of the top (atrial) or bottom (ventricular) of the heart may be associated with risk (or may be of no significant concern). Formal evaluation by a cardiologist is needed to make this determination.
FAQ
What is a heart screening?
What is sudden cardiac death (SCD)?
What heart conditions are screened for at an Augustheart Screening?
HYPERTROPHIC CARDIOMYOPATHY (HCM): This is a problem of the heart muscle where the bottom chambers (or ventricles) are too thick. The risk of this condition has been reported to be as frequent as 1 in 500 individuals.
DILATED CARDIOMYOPATHY: This is a problem where the heart muscle is too large and does not squeeze as it is supposed to. The risk of this condition is estimated to be 1 in 2,000 individuals.
AORTIC ROOT ANEURYSM: This is a problem of an abnormal enlargement of the main artery that arises from the heart and is responsible for delivering oxygenated blood to the body. The risk of this condition is estimated to be 1 in 10,000 individuals.
LONG QT SYNDROME: This is a problem of the electricity of the heart that is caused by an issue with how the heart muscle handles essential elements like sodium and potassium. Children with this condition can suddenly develop unstable heart rhythms. The risk is as high as 1 in 5,000 individuals.
WOLFF-PARKINSON-WHITE (WPW) SYNDROME: This is a problem of the electricity of the heart that is caused by an abnormal connection between the top and bottom pumping chambers. This condition can cause very fast heartbeats and, rarely, an unstable heart rhythm. The risk of this condition has been reported to be as frequent as 1 in 1,500 individuals.
What is an echocardiogram (ECHO)?
What is an electrocardiogram (ECG)?
Why may both ECG and limited ECHO tests be necessary?
Does University Interscholastic League (UIL) require heart testing on all athletes?
Why screen students 14 to 18 years of age?
How long will the screening last?
What should the student bring to the event?
If you can’t fill the form out online, students should bring a signed AugustHeart consent waiver with them to the event (OR) be accompanied by a parent/guardian who can sign a consent waiver available at the venue.
Download English waiver here >
Download Spanish waiver here >
What should the student wear to the screening?
Should the student be accompanied by a parent?
Download English waiver here >
Download Spanish waiver here >